- info@routeoptimizationconsultants.com
- 1751 Pinnacle Dr #600d, McLean, VA 22102
- Monday to Friday 9:00AM - 5:00PM
- Let’s Talk: (571) 316-0676
Mobile Workforce Management
- Home
- Mobile Workforce Management
Mobile Workforce Management Solution Areas
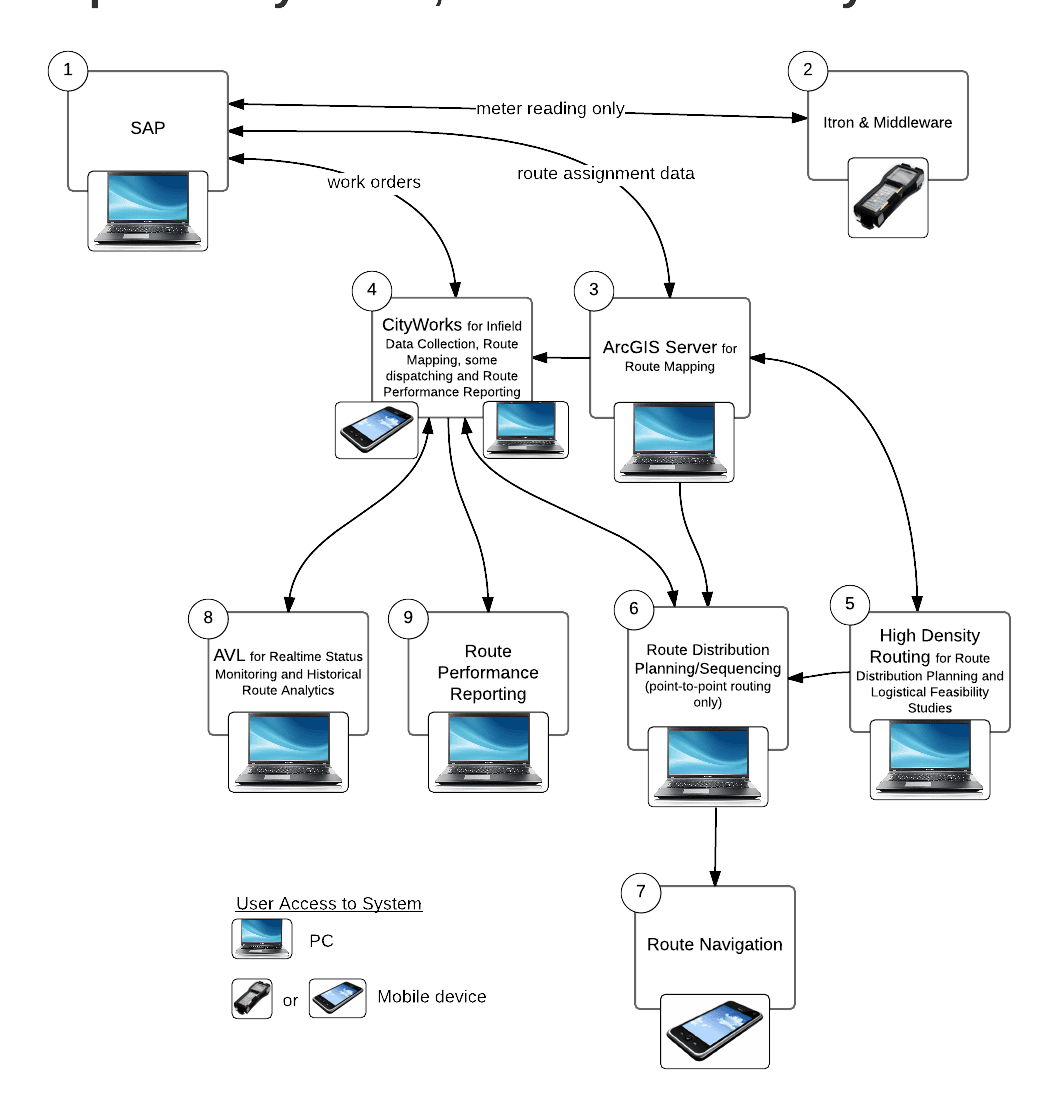
Provided below is a summary of an assessment for the current and potential future mobile workforce management systems from a recent client, a large municipal utility with over 160 crews dispatched daily for managing the water system and solid waste collection.
Summary of Solution Areas and Descriptions
|
Summary of Solution Areas and Descriptions |
|
| Solution Area | Description |
| Route Distribution Planning | A system that defines the schedule for the stops and assigns the stops to a route, but does not define the sequence that the stop should be serviced. The schedule is the day or time window of service. The route boundary is the geographic extent of the route assigned by the Route Distribution system. A route boundary may be condensed and all stops are required to be contiguous, such as in a waste collection route or meter reading route, to reduce travel time between stops or customers (and make it easier for the crews to remember). A route boundary or zones may be spread out over the entire City, such as for water quality, line maintenance or cart deliveries.
System types include: high density and point-to-point route optimization software; GIS; route management systems; and dispatching software. In practice, high density route optimization software typically only gets used for Route Distribution Planning. |
| Route Sequencing | A system that defines the sequence that every stop should be serviced in a route. A sequence refers to the order that the stops are visited in the route. In cases of high density routing, like waste collection routing, the sequence would seem very important. In reality, the drivers have a multitude of preferences and safety issues that the route optimization software does not know. Thus, the sequence for waste routing is not critical, but the distribution (schedule and boundary) is critical. However, for cart deliveries, the optimized sequence is critical and the boundary is not as important.
System types include: high density and point-to-point route optimization software or add-on modules for point-to-point routing with ERP and asset management systems. |
| Route Update Notification | A system to notify the route managers that there are new stops or work orders to be added to routes. This may occur as a periodic event (such as, annual to daily) or dynamically in real time. |
| Route/Work Order Mapping | A system to display points on a map of the locations for work orders or stops. |
| Dispatching | A system to manage the assignment of staff, crews and equipment to routes and work orders. Rules may be applied to the system to automatically assign work orders to a crew or the assignment may be done via a route optimization software. Rules that may be used include zones, first come first serve, priority by type, etc. Either by rule or route optimization, the dispatcher using the software will review and modify the assignments, as needed. |
| Route Navigation | A system to provide turn by turn directions to each stop or work order. Systems use GPS and either installed software or web-based applications to provide the directions. |
| Route Status Monitoring | A system to visually display on map the location of crews on a route. The system may also include the ability to see when a stop has been visited by a crew. If route sequencing is employed, the system may also allow for predicting when the stop will be serviced in the future. If Infield Data Collection is employed the system may be able to provide verification of when the stop has been serviced or the work was completed.
Systems are typically referred to as automatic vehicle location (AVL), which use GPS to automatically determine the geographic location of a vehicle and transmits this information back to a central server using SMS, GPRS, satellite or terrestrial radio. |
| Infield Data Collection | A system to collect data in the field regarding work order or service that was conducted, verifying the service was conducted, issues with completing the service, or other data relevant to the field work. |
| Route Performance Reporting | A system to capture, compile and report on the productivity of routes and the crews. Travel times, services times, disposal times, pre-post trip times, break times may all be collected. Other data to be collected may include weights, equipment, materials, and costs. The system may be a standalone database that has data manually entered after the route is complete or it may be a component of a route management or mobile workforce management system. This may also include cost reporting, whether that be the more extensive activity based costing or more simplified route costing only based on the in-field costs and excluding administrative and maintenance costs. |
| Historical Route Analytics | A system to compile, analyze, and report on the proximity, travel path, time, and distance that a route was run on a given day or as an average over a time period. This system is typically a functionality of an AVL system used for Route Status Monitoring. |
| Logistical Feasibility Analysis | A system that allows for analyzing what if scenarios related to crews, routes and facilities. This system is typically a functionality of a route optimization software used for Route Distribution Planning. Mobile workforce management systems also provide some logistical analyses related to crew productivity. |
Types of Route Optimization Solutions
Specific to the City’s opportunities for route optimization, the City has three types of routing problems to solve:- Planned Routes – With a fixed number of stops that has a very low percentage of changes to the stops on a daily basis, planned routes may be updated annually or semi-annually. Examples are automated residential waste collection, bulky waste collection, and meter reading.
- Dynamic Routes – The stops to be serviced varies on a daily basis and may change during the day as new work orders are created. Examples are waste cart deliveries and line maintenance.
- Combined Planned and Dynamic Routes – The crews have a fixed number of stops with work order stops added in at the beginning of the day and during the day. Examples include water flushing, meter repairs/maintenance, and water quality laboratory sampling.
Mobile Workforce Management Systems
Although definitions vary by vendor, mobile workforce management systems (WFM) generally encompass the above listed Solution Areas with some exceptions. Mobile workforce management systems are a combination of business processes, software and mobile devices used to improve productivity of its field service employees and their associated back office. WFM integrates resource planning, scheduling, dispatch, mobile, and business analytics. The only aspect of the Solution Areas that have not been integrated into these suites of applications and devices has been high density residential routing, which is generally a planned task, whereas, the mobile workforce is regarding the optimization of the daily dynamic work in the field. Components of WFM systems are offered by current City software vendors, SAP, Kronos, CityWorks, and ESRI. There are WFM solutions from vendors solely focused on WFM. There are a myriad of apps and systems being offered for the Solution Areas that also consider themselves to be WFM. WFM is a relatively new and dynamically evolving technology arena with limited standardization.Typical Municipal Utility Systems
Current
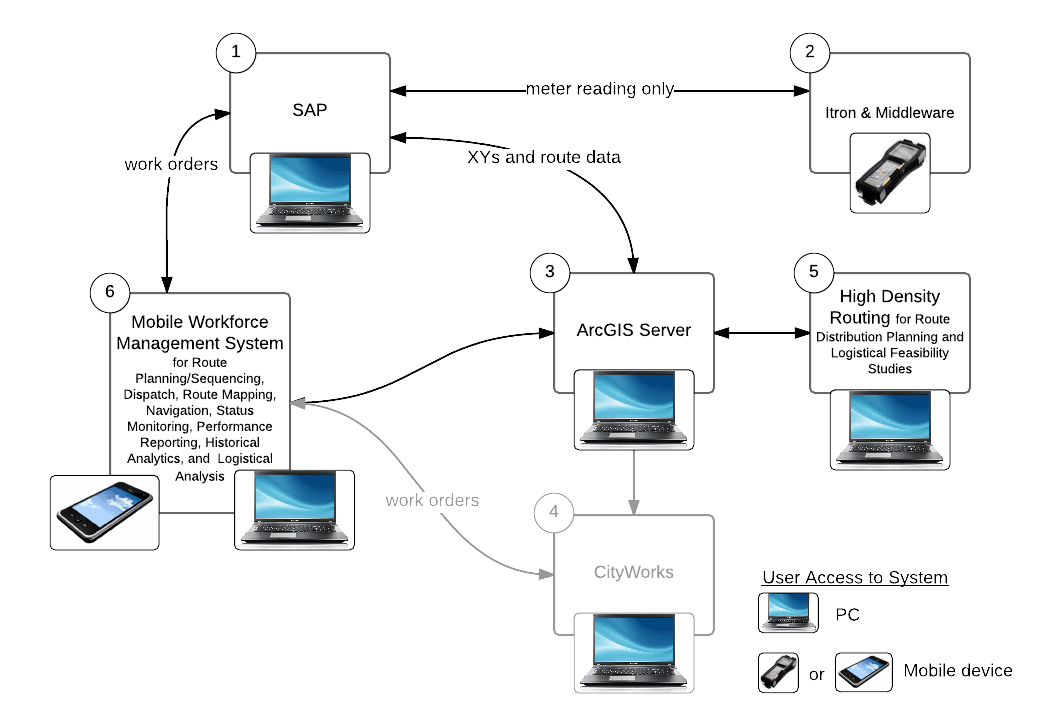
Proposed System 1 – Comprehensive Solution Suite
A Comprehensive Solution Suite system minimizes the number of disparate systems by accomplishing most of the requirements via one mobile workforce management system (WFM). WFM becomes the primary system for managing field services. High density routing is the only system that is also added. Integrations between WFM, SAP and ArcGIS Server provide the foundation for consistency between work order, route and asset/customer data.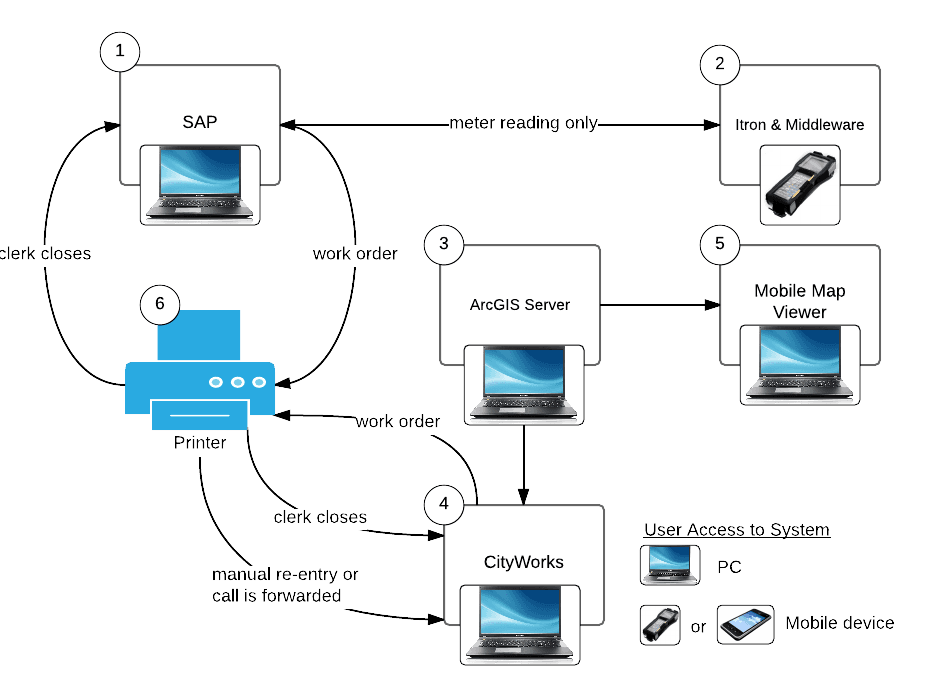
Proposed System 2 – Disparate Systems
A Disparate System maximizes the utilization of existing systems, but is based on adding new systems that are solutions that Cityworks can provide. Cityworks becomes the primary system for managing field services. Significant integration is required. The main challenge with this approach is the integration between SAP and Cityworks.